1. Differences in U-Joint Applications Between BMW and Kawasaki
U-joints serve as critical components in both BMW and Kawasaki vehicles, albeit with distinct engineering approaches tailored to their respective product lines and performance requirements.
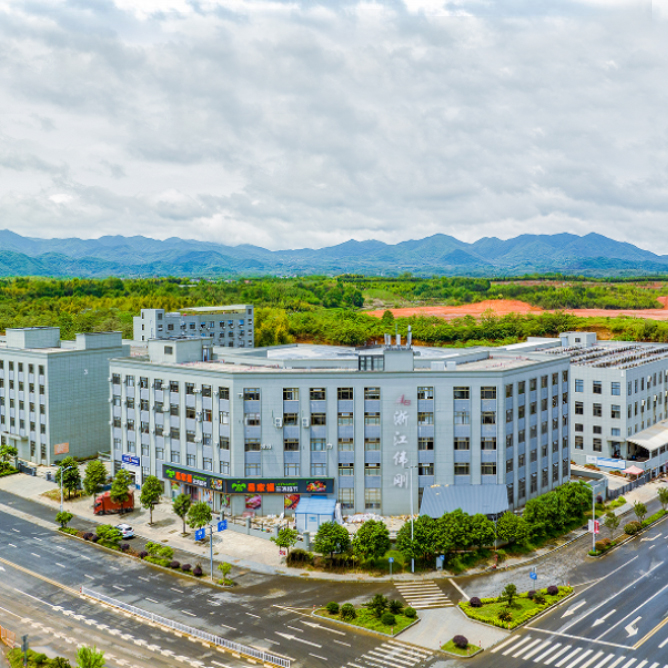
BMW: BMW, renowned for its focus on precision engineering and performance, incorporates U-joints that emphasize durability and efficiency. In BMW motorcycles and cars, U-joints are meticulously engineered to withstand high torque outputs while maintaining smooth power transmission. Materials such as alloy steels are often utilized for their strength and resistance to fatigue under dynamic conditions. BMW’s design philosophy often integrates advanced sealing technologies to enhance longevity and minimize maintenance intervals, reflecting their commitment to quality and reliability in every aspect of drivetrain design.
Kawasaki: In contrast, Kawasaki’s approach to U-joint applications reflects a blend of robustness and adaptability across a diverse range of motorcycle and automotive models. Kawasaki vehicles often feature U-joints that prioritize resilience to varying operating conditions, including off-road environments and high-performance sport applications. The design considerations include optimal balance between strength and weight, leveraging materials like high-strength alloy steels or specialized composites to achieve durability without compromising agility or responsiveness. Kawasaki’s U-joint designs are tailored to support a wide spectrum of riding styles and driving dynamics, ensuring reliability under demanding usage scenarios typical in both recreational and professional settings.
Both BMW and Kawasaki integrate U-joints as integral components within their drivetrain systems, albeit with nuanced differences to meet specific vehicle requirements. BMW’s emphasis on precision and performance engineering aligns with their brand’s commitment to delivering exceptional driving experiences across their motorcycle and car lineup. In contrast, Kawasaki’s approach prioritizes robustness and adaptability, ensuring their U-joints can endure diverse operational challenges while maintaining the agility and responsiveness synonymous with their vehicles.
2. Common U-Joint Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance of universal joints (U-joints) is essential to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of both motorcycle and car drivetrains. Proper care not only extends the lifespan of U-joints but also prevents costly repairs and potential drivetrain failures. Here are some key practices:
a)Inspection and Lubrication Schedule: Routine inspections are crucial to detect early signs of wear or damage in U-joints. Visual checks should include looking for signs of rust, cracks, or excessive play in the joint. It’s recommended to inspect U-joints during scheduled maintenance intervals or whenever the vehicle undergoes service. Lubrication plays a critical role in U-joint longevity.
b)Symptom Monitoring: Monitoring for symptoms such as vibrations, clunking noises, or unusual steering responses can indicate U-joint wear or failure. Addressing these symptoms promptly can prevent further damage to other drivetrain components. Periodically checking for vibrations during acceleration or deceleration, particularly in vehicles with high mileage or heavy usage, is advisable.
c)Replacement and Repair: When signs of wear or damage are detected, U-joints should be promptly replaced or repaired by qualified technicians. Replacement intervals vary depending on vehicle usage, environmental conditions,. It’s crucial to use OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure compatibility and performance.
d)Environmental Considerations: U-joints exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as saltwater or extreme temperatures, require more frequent inspection and maintenance. Corrosion-resistant coatings or materials may be recommended for vehicles operating in coastal areas or regions with harsh winters.
e)Preventive Measures: Implementing preventive measures can mitigate U-joint wear. These include avoiding excessive loads or towing beyond vehicle specifications, minimizing sudden accelerations or decelerations, and maintaining proper wheel alignment to reduce stress on U-joints.